The whole month of October is National Cybersecurity Awareness month, which is the perfect time to reflect on past strategies and get better protected. This month, take time to look at your current cybersecurity strategy and determine whether your business can identify, detect and respond to threats appropriately. If not, it is time to get informed and protected.
According to a study sponsored by IBM Security and conducted by Ponemon Institute, the 2018 Cost of a Data Breach Study found that the average cost of a data breach globally has reached $3.86 million, a 6.4 percent increase from the 2017 report.
If you do not have a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy involving technology, people, and your processes, you could be a risk. Do you know the biggest threats to your cyber security and how to fight them? The “2018 Verizon Data Breach Investigation Report” (DBIR) is a great starting point.
Current Cybersecurity Breach Threats
In 2018 cyber criminals are still finding success with the same tried and tested techniques they’ve used in recent years. This means that their victims are still making the same mistakes too. Most cybersecurity breaches are incited by a criminal who is motivated by money. In fact, Verizon’s 2018 Data Breach Report found that 76 percent of breaches were financially motivated.
Keep in mind, not all the cybercriminals are outsiders. It turns out that over a quarter of attacks come from insider threats. That means 28 percent of breaches can come from a trusted employee, partner or vendor. It is important to understand who has access to your critical data and restrict it to only those who absolutely need it.
Top Cybersecurity Risk for Each Industry:
While there are similar threats that each industry faces, many sectors face their own set of unique challenges. It is important to understand those unique threats and create a strategy of prevention around them. Here is a brief look at 11 different industry’s top cybersecurity threats:
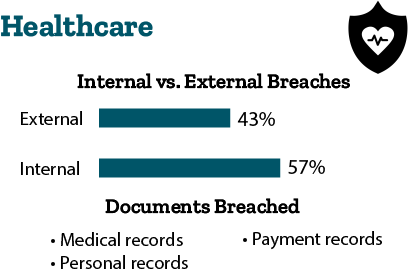
- Healthcare: 43 percent of breaches are external, and 57 percent of breaches are internal. Cybercriminals are breaching medical records, personal records, and payment records. They are doing so through misuse of documents and human error. Healthcare is the only industry where the threat from inside is greater than that from outside.
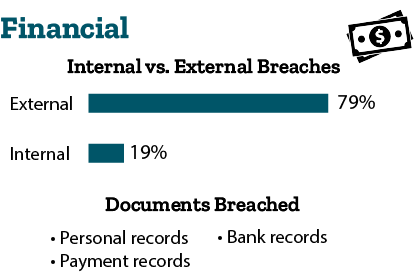
- Financial: 79 percent of breaches are external, and 19 percent of breaches are internal. Cybercriminals are breaching personal records, payment records, and bank records. They are doing so through hacking and physical action. Payment card skimmers are still a major threat and can be installed on ATMs by organized criminal groups.
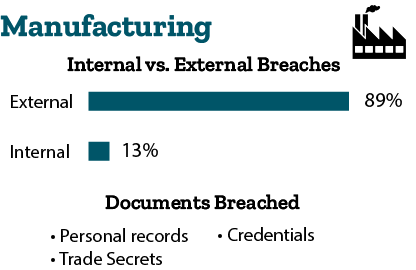
- Manufacturing: 89 percent of breaches are external, and 13 percent of breaches are internal. Cybercriminals are breaching personal records, trade secrets, and credentials. They are doing so through hacking and malware. In the manufacturing industry, almost half of the breaches are motivated by intellectual property to gain a competitive advantage.
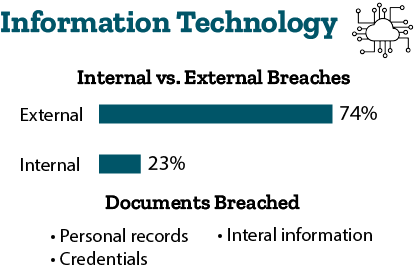
- Information Technology: 74 percent of breaches are external, and 23 percent of breaches are internal. Cybercriminals are breaching personal information, credentials, and internal information. They are doing so through hacking and human error.
- Retail: 91 percent of breaches are external, and 10 percent of breaches are internal. Cybercriminals are breaching payment information, personal information, and credentials. They are doing so through hacking and physical action. In the retail industry web application attacks leveraging poor validation of inputs or stolen credentials is the top concern.
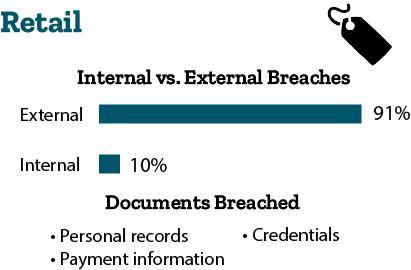
- Professional Services: 70 percent of breaches are external, and 31 percent of breaches are internal. Cybercriminals are breaching personal information, credentials, and internal information. They are doing so through hacking and social attacks. Attacks are typically financially motivated and often involve phishing or the use of stolen credentials in the professional services industry.
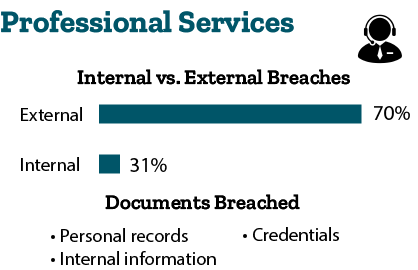
- Accommodation and Food Services: 99 percent of breaches are external, and 1 percent of breaches are internal. Cybercriminals are breaching payment information, personal information, and credentials. They are doing so through hacking and malware. The Accommodation industry is over 100 times more likely than the median industry to have a POS controller targeted.
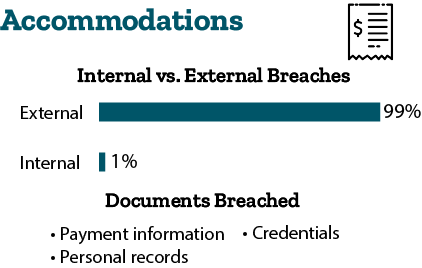
- Education: 81 percent of breaches are external, and 19 percent of breaches are internal. Cybercriminals are breaching personal information, trade secrets, and medical records. They are doing so through hacking and social attacks. The Education sector’s highly sensitive research is at risk with 20 percent of attacks motivated by espionage.
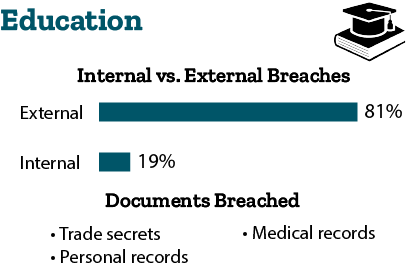
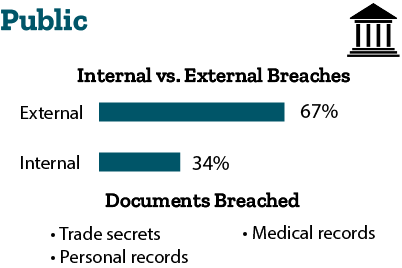
- Public: 67 percent of breaches are external, and 34 percent of breaches are internal. Cybercriminals are breaching personal information, trade secrets, and medical records. They are doing so through hacking and social attacks. Cyber-espionage is a major concern for the public sector, as 44 percent of breaches are motivated by espionage.
Data Breach Timelines
When breaches are successful, it only takes a short time to compromise data. The time from the first action in a breach to the initial compromise of an asset is often measured in seconds or minutes. Unfortunately, the time it takes for a company to discover a breach is measured in weeks, months, or even years. In this time, cybercriminals can get the information they need without being detected.
To prevent or survive a cybersecurity breach, focus on understanding what types of data that are likely to target. From there, figure out the applications and controls you have in place to make it difficult to access and exfiltrate.
Breach Responses for Better Outcomes
Having the goal to completely evade a breach is not plausible. It is important to have a backup and response plan for when your company does encounter a cybersecurity breach. The single most important factor which determines the outcome of making a successful recovery after a breach is the speed of response.
Regardless of motive, response to a data breach must be swift. It is important to notify parties involved immediately so a response team can secure the necessary evidence to identify the criminal, recover assets and minimize reputational impact of a breach.
How to Mitigate Cybersecurity Risks
With all the different tactics that cybercriminals are taking, it’s more important than ever to be vigilant and make changes now. Your company can start by limiting software installations and developing proper password procedures. Make sure you only allow connections from whitelisted IP address and be sure to filter remote access to your POS network.
A common cybersecurity threat that many industries above are facing includes the stealing of internal information or trade secrets. If your organization has highly sensitive information, keep it separate and only allow access to those who require it to perform their job. This can also help to lower the risk of human error or internal threats. Each industry should also have a current business continuity or disaster recovery plan in place if suspicious activity or a breach occurs.
It is also important to remember physical security. Not all data breaches occur online. Surveillance cameras and entry systems for restricted areas can help avoid criminals from stealing or tampering with sensitive material.
People Make Mistakes
While companies do have employees that cause data breaches that are motivated by malicious intent, many internal breaches are caused by human error. In fact, almost one in five data breaches are due to errors. This includes employees sending an email to the wrong person, failing to shred confidential information, or accidentally clicking on a phishing email.
Human error is not a new concept. It continues to be a major problem in regard to cybersecurity year after year. Many employees continue to fall for phishing emails. Strangely enough, the more phishing emails someone has clicked, the more likely they are to do so again.
Beware of Ransomware
More and more we are witnessing cybercriminals using ransomware to keep companies from using their data. This year, it is the most prevalent variety of malware used. According to the DBIR, ransomware is the top variety of malicious software, found in 39 percent of cases where malware was identified.
Ransomware is easy to deploy and can be effective for the most amateur of cybercriminals. Increasingly, cybercriminals are not looking to just encrypt single user devices. They are going after corporations and even entire industries. Criminals are making more money when they can encrypt entire databases. If your company is not currently backed up, criminals could take your business offline.
Predict What Cybercriminals Will Do Next
The DBIR includes ten “Incident Patterns” that can help predict a cybercriminal’s next move. Understanding these areas of concern will be an asset to your security professionals when deciding where and how to invest resources if they are limited. The ten incident patterns are:
- Web Applications
- Miscellaneous Errors
- Point of Sale
- Privilege Misuse
- Cyber-Espionage
- Lost and Stolen Assets
- Crimeware
- Payment Card Skimmers
- Denial of Service
- Everything Else
Who Is Attacking You?
Cybercriminals come from many different sources. In addition to understanding the specific threats related to your business industry, it is critical to know who is behind those breaches. According to the 2018 DBIR there were numerous sources behind last year’s breaches.
- 73 percent were perpetrated by outsiders
- 28 percent involved internal actors
- 2 percent involved partners
- 2 percent featured multiple parties
- 50 percent of breaches were carried out by organized criminal groups
- 12 percent of breaches involved actors identified as nation-state or state-affiliated
While there seems to be a variety of attackers, there are commonalities between their tactics, victims and motivations. Those commonalities include the use of non-POS malware installed through a malicious email and how breaches took months or longer to discover.
Other commonalities included that cybercriminals were financially motivated, or they were motivated by the gain of a competitive or strategic advantage. Some common tactics being used by cybercriminals include hacking, malware, social attacks, privilege misuse or physical action.
Calculating the Cost of a Breach
According to IBM, in the past five years, the amount of mega data breaches has nearly doubled from just nine in 2013 to 16 mega breaches in 2017. For data breaches, the biggest cost category is loss of business. Other costs can be from legal and regulatory fees, technology and services needed to recover from the breach, and compensations made to customers.
Impacting Costs of a Data Breach
The 2018 Ponemon Institute Cost of a Data Breach Study examined the factors that can increase or decrease the cost of a breach. They found that costs are impacted by the amount of time spent containing a data breach and investments in technologies that speed up response time. They also found:
- The average time to identify a data breach in their study was 197 days, and the average time to contain a data breach once identified was 69 days.
- Companies who contained a breach in less than 30 days saved over $1 million compared to those that took more than 30 days
National Cybersecurity Month
National Cybersecurity Month was created by the National Cybersecurity Alliance and the U.S. Department of Homeland Security in October 2004. Each week during National Cybersecurity Month focuses on different themes that address specific challenges and help to identify opportunities for change.
This year’s National Cybersecurity Month has addressed specific challenges and identified opportunities for behavioral change. It highlighted the need to build a strong cyber secure workforce to help ensure businesses’ infrastructure is better protected.
There is still time to get involved. You can start by following the National Cybersecurity Alliance on Twitter, Facebook, YouTube and LinkedIn to receive the latest online safety news and resources. You can also continue to start conversations with coworkers or others in the community about security best practices.
Get the Right Cyber Protection
No matter the level of protection, no system is 100 percent secure from cybercriminals. However, with a solid understanding of the threats you face and the knowledge to combat them, you can improve your cybersecurity strategy. Now is not the time to ease up. Cybercriminals are constantly working to access your private information. They are using every tool at their disposal to take advantage of your vulnerabilities, from human error to weak infrastructure.
Now that you’re aware, it is time to defend your company. LightEdge specializes in high security hosting and compliance for all organizations. Our expertise is especially valuable to those with sensitive data, such as the healthcare and financial industries.
LightEdge has designed security and compliance into each of our Des Moines, Kansas City, Omaha, and newly acquired Austin and Raleigh data center facilities.
Each of our LightEdge facilities strive to deliver more than traditional data centers. We have created true Hybrid Solution Centers designed to offer a complete portfolio of high speed, secure, redundant, local cloud services and managed gateways to public clouds through our hardened facilities.
Contact one of LightEdge’s highly skilled cybersecurity and compliance experts here to discuss how we can protect your valuable data, together.
Related Posts
- How to Develop an Effective Cybersecurity Recovery Plan
- Weighing the Cost of Data Security: Why It’s Important For Large and Small Businesses
- Balancing Data Breach Prevention and Response Planning
- 6 Ways to Noticeably Heighten Healthcare Data Security
- PCI Compliance: Everything You Need To Know About Payment Security
- 4 Best Practices for Cybersecurity and Data Protection in Education




